IKS04
IKS04 is the first 'ultra-low DAR' ADC in development for solid tumors
IKS04 is currently in late preclinical development with IND anticipated by Q4 2024/ Q1 2025. It represents a new approach for the treatment of GI cancers and is the only CA242-directed ADC in development.
Development status
Differentiation by design
Iksuda's IKS04 program has been designed to overcome challenges often associated with targeting therapies in solid tumors. IKS04 is comprised of an anti-CA242 antibody, engineered for site-specific conjugation of PBD prodrug payloads, DNA-cross-linking being a more relevant mechanism for these highly difficult-to-treat cancers, especially colon adenocarcinomas.
Tumor-selective activation and release is vital for the safe delivery of these highly potent payloads. In pre-clinical testing, IKS04 is associated with the highest TI for any PBD-containing ADC directed towards solid tumors.
In addition, IKS04 will be administered via a unique dose regimen for ADCs, with pre-administration of naked antibody akin to radiotherapies.
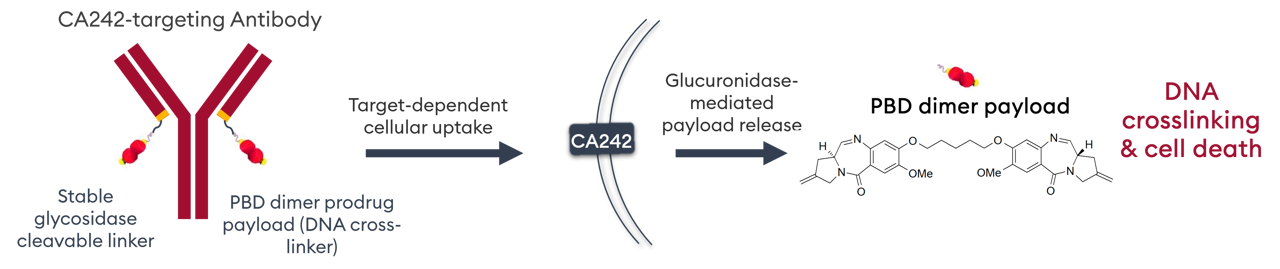
A beta-glucuronide linker is used for tumor-selective payload release, whilst a second beta-glucuronide moiety improves hydrophilicity and plasma stability of the PBD prodrug.
Payload release and ADC activation requires processing by beta-glucuronidase, an enzyme overexpressed in cancer cell lysosomes, active only at acidic pH and with low expression in normal tissues.
Creating a perfect storm of positivity for cancer patients
However, such payloads need to be delivered precisely and be associated with a suitable safety & efficacy profile. Iksuda’s ADCs utilize tumor-selective activation and release of payloads, currently through the incorporation of beta-glucuronide (BG) linkers and triggers.
Our IKS03 program demonstrates the potential of the PBD prodrug approach as a suitable option for hard-to-treat solid tumors. This ADC contains a highly potent, talirine-like PBD, safely delivered via the BG-driven mechanism. In preclinical studies, tumor-selective delivery drives class leading efficacy and safety, resulting in significantly enhanced TI. ADC design is also associated with bystander effect, suggesting that solid tumors with heterogeneous/ low expression may also benefit.
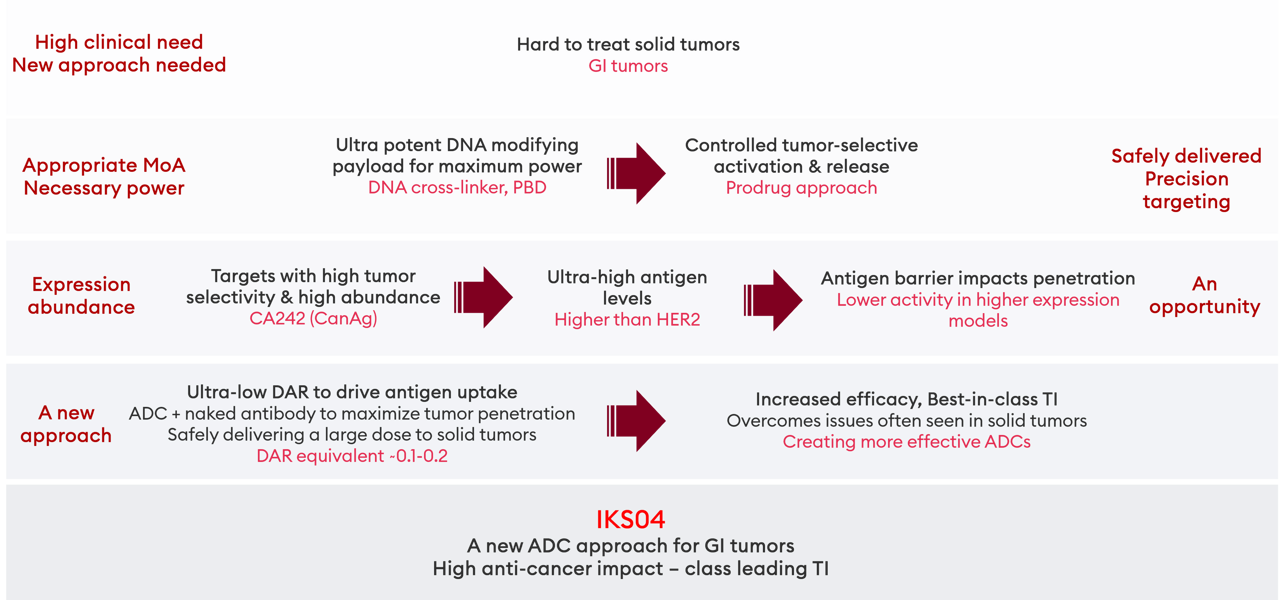
For our IKS04 program, Iksuda considered antigen targets for GI tumors which are associated with high expression abundance and high tumor selectivity: CA242 (CanAg) represents the most appropriate choice.
IKS04 is therefore comprised of an anti-CanAg antibody engineered for site-specific conjugation of a PBD prodrug, where a BG linker is used for tumor-selective payload release, and a second BG moiety improves hydrophilicity and provides added reassurance against unwanted binding to proteins in plasma. β-glucoronide is overexpressed in cancer cell lysosomes, active only at acidic pH and with low expression in normal tissues.
Ultra-low DAR approach
Due to the high abundance in CanAg-high expressing models – higher than that seen with HER2 – an antigen barrier lowers tumor penetration and ADC efficacy compared with CanAg-low models. CanAg represents a perfect target for an ultra-low DAR approach.
In preclinical studies, IKS04, administered as a single dose, induces impressive efficacy across a range of CanAg-expressing models and GI tumors – significantly higher than the clinical benchmark ADC cantuzumab ravtansine, (a CanAg-directed ADC which was suspended during clinical trials by Immunogen due to a sub-optimal profile) in all xenografts tested.
However, activity is highest in low-expressing models and lowest in high-expressing models suggesting that high expression abundance impacts tumor penetration.
For this antigen, the high CanAg-expressing Colo205 (colorectal adenocarcinoma) and SNU16 (gastric adenocarcinoma) models, the copies/ cell are ultra-high compared with typical targets, at up to 11.5 million. This is even greater than HER2, though far more tumor-specific.
The addition of naked anti-CanAg antibody to IKS04 significantly reduces MED in high- and very high-expressing models with minimal impact on the efficacy observed for the ADC in low-expressing models.
Importantly, this enhancement in efficacy does not negatively impact toxicity thresholds. In toxicology studies in rats and non-human primates, ultra-low DAR IKS04 is associated with a favorable, clinically desirable TI.
IKS04: a new approach for hard-to-treat GI cancers |
Highly potent proPBD payload with tumor-selective activation |
Highly tumor-specific, high density GI cancer target; CA242 |
Site-specific homogeneous conjugation |
Ultra-low DAR to overcome tumor penetration/ payload delivery challenges for high potency payloads |
Class leading TI |
Keep informed
Sign up for our latest programme news and insights