Tumour-selective Payload Activation
All Iksuda’s ADCs benefit from tumor-selective activation and release of payload for added safety.
Iksuda's prodrug approach is driven by the use of β-glucuronide (BG) linkers and triggers, ensuring that the payload is only released in cancer cells and avoiding the risk of on-target, off-site toxicity.
β-glucuronidase is overexpressed in cancer cell lysosomes, is active at acidic pH and has low expression in healthy tissues.
The BG-driven prodrug approach is now clinically validated
IKS014 (HER2-directed ADC) is currently in Phase 2 trials in China, where it is under license to Fosun as FS-1502.
Phase 1 studies have confirmed that the BG linker platform drives a differentiated and improved safety profile over other HER2-directed therapies. With equivalent efficacy to Enhertu, this ADC is not associated with dose-limiting respiratory toxicities, neutropenia or ocular toxicity. There is a notable absence in other events frequently seen in HER2-targeting therapies such as nausea, vomiting and severe fatigue.
Tumor-selective activation & release of the right payload drives a differentiated clinical profile
Unlike traditional MMAF-asociated ADCs, IKS014 (FS-1502) shows a marked reduction in dose-related ocular toxicities and an absensce of those associated with the cornea. There is a distinct difference in ILD and neutropenias compared with Enhertu and marked reduction in thrombocytopenia compared with Kadcyla.
Data presented at SABCS 2023: data cut-off December 2022 after a median follow up of 5.2 months.

Tumor-selective payload release and activation for added safety
We match payload MoA with clinical indications based on our payload platform expertise. Through our prodrug linker formats, we are able to deliver the most relevant and potent payloads with precision, avoiding on-target, off-site toxicities.
After payload release, there is no trace of linker attachment, and this traceless chemistry allows use with multiple payload classes.
Iksuda uses the BG linker/ trigger approach alongside all payload mechanisms. It is compatible with known classes such as auristatins, DNA cross-linkers and topoisomerase I inhibitors, as well as novel classes such as next-generation auristatins (cryptophycins), DNA monoalkylators, Iksuda’s proprietary ‘ProAlk’ payload class of protein alkylators and anthracyclines.
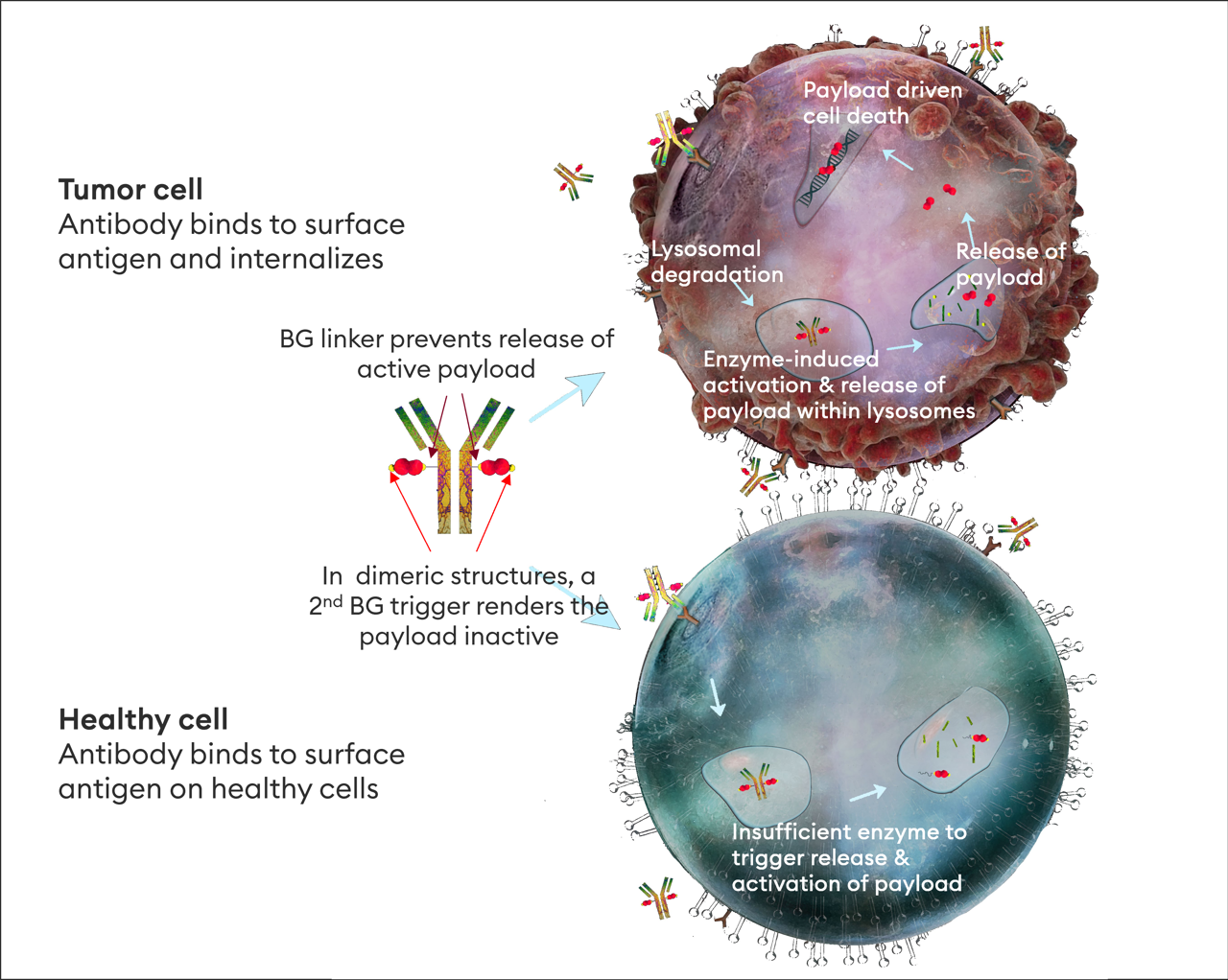
Tumor-selective payload release drives a differentiated ADC profile
The BG linker/ trigger format leads to superior efficacy and wider tolerability than clinical benchmarks
For example, Iksuda’s CD19-directed ADC IKS03 demonstrates an order of magnitude improved differential in tumor vs normal cell killing compared with the clinical benchmark SGN19B.
SGN19B induces total B-cell depletion at doses below its effective dose whereas IKS03 does not induce complete B-cell depletion at doses far in excess of its effective dose. This supports the hypothesis of differentiated tumor cell activation of linker/ payload due to the difference in glucoronidase activity. 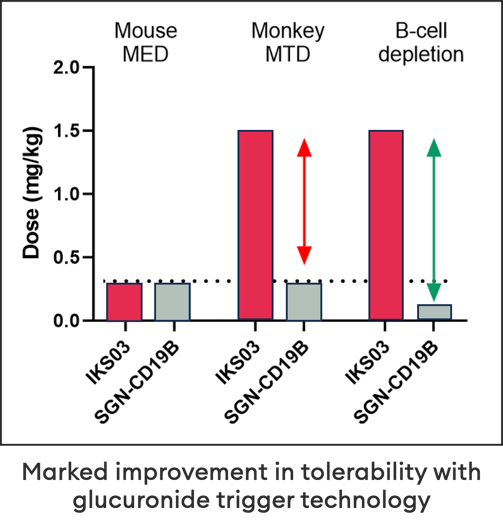
Expanding clinical utility of tumor-selective payload activation

Contact us about partnerships for ADC design & development
